Glossary
Refer to this list of terms and concepts as you review the content of RVAgreen 2050. Email us if there is a word or phase you would like to see added to this list!
ADA compliant sidewalks
Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) compliant sidewalks possess a number of features that make them more accessible to individuals with disabilities. Standards define appropriate sidewalk width, surface texture, trip hazards, slope, and the availability of curb ramps.
Air Quality Index
Air Quality Index (AQI) is the nationally recognized indicator for reporting air quality. It runs from 0 to 500, and higher AQI values signify greater levels of air pollution and greater health concerns. A value below 50 (green) generally indicates good air quality, while a value above 300 (maroon) is hazardous.
Anti-idling
Motor vehicle emissions make up a significant portion of most cities' emissions. Anti-idling laws aim to reduce these emissions by requiring motorists to turn of their engines when parked, stopped, or standing for more than a set amount of time (three minutes, for example).
anaerobic digestion
Anaerobic digestion is the process through which bacteria break down organic matter - which includes animal manure, biosolids, and food wastes - in an environment that lacks oxygen (usually a sealed vessel).
BEV/HEV vehicles
BEVs are Battery Electric Vehicles, which are powered solely by an electric battery with no gas engine parts. HEVs are Hybrid Electric Vehicles, which use an electric motor to assist gas-powered engines and all energy comes from gasoline.
bike-friendly infrastructure
Bike-friendly infrastructure is part of a "complete street" that is accessible and safe for all pedestrians, cyclists, public transit, and vehicles. It includes bikeways, lanes for bikes, shared use and quiet-street bike routes, painted buffer lanes, and conventional bike lanes, among others.
blower duct/duct leakage testing
Blower door and duct leakage tests measure the air flow that passes through a duct system. These tests can help to identify inefficiencies and make repairs that will lead to lower energy bills, improved air quality, and better performance.
carbon sequestration
Carbon sequestration is the process for capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide, used to reduce the overall amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and reduce the effects of global warming.
clean energy
Clean energy is energy derived from renewable, zero-emissions sources, as well as energy saved through energy efficiency measures. Renewable energy comes from natural processes, and energy efficiency reduces the amount of energy required. A clean energy economy powered by both renewables and energy efficiency is the most sustainable energy planning scenario.
circular economy
Circular economies share three principles: design out waste and pollution, keep products and materials in use, and regenerate natural systems. These circular economies aim to gradually decouple economic activity from the consumption of finite resources by promoting waste reduction and materials reuse.
climate neutral
Climate neutrality is achieved by balancing the amount of emissions generated with Earth's natural capacity to absorb them. It does not necessarily mean zero emissions, but reaching an equilibrium between emissions and absorptive capacity.
combined heat and power (CHP)
Combined heat and power (CHP) is an energy efficient technology that generates electricity and captures the heat that would otherwise be wasted to provide thermal energy used for heating, such as steam or hot water. CHP can work at an individual facility or building and be used in both residential and industrial processes, though it is most common in industrial settings.
composting
Composting is the natural process of recycling organic matter (leaves, food scraps) into a fertilizer. Anything that grows can decompose and composting helps to speed up this process.
design phase
The design phase is the design of a building construction or renovation project, inclusive of the issuance of a request for proposal and the project budget approval.
energy burden
Energy burden means the percentage of household income that goes toward energy costs. Low income, African American, Latino, and people who rent often have a much higher energy burden than the average household.
energy efficient retrofits
Retrofits for energy can include improvements or modifications that may improve energy efficiency or decrease energy demand. These have the potential to reduce operational costs and help meet market expectations for newer buildings.
Energy Star standards
Energy Star standards are government-based benchmarks for energy efficiency in over 70 products.
EnergyCap
EnergyCAP is an energy management and utility bill software that allows users to benchmark buildings, analyze energy data use, and automate many accounting and management tasks.
environmental justice
Environmental justice is the fair treatment and meaningful involvement of all people – regardless of race, color, national origin, or income – with respect to the development, implementation and enforcement of environmental laws, regulations and policies. No group should bear a disproportionate share of negative environmental impacts resulting from industrial, governmental and commercial operations or policies.
equity
The term “equity” refers to fairness and justice and is distinguished from equality: While equality means providing the same to all, equity means recognizing that we do not all start from the same place and must acknowledge and make adjustments to imbalances. The process is ongoing, requiring identifying and overcoming intentional and unintentional barriers arising from bias or systemic structures.
e-waste
E-waste, short for electronic waste, refers to electronic products that are nearing the end of their useful life. Certain components of e-waste contain materials that can make them hazardous to human and environmental health.
food waste diversion
Food waste diversion aims to redirect organic waste from the landfill and use it as a more useful resource. Food waste in landfills can contribute to global warming by emissions of carbon dioxide and methane gas that are released as it breaks down.
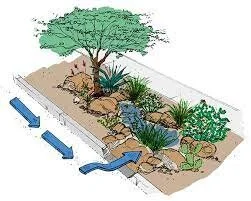
green infrastructure
Green infrastructure is any of a range of measures that use plant or soil systems, permeable pavement (or other substrates), stormwater harvest and reuse, or landscaping to store, infiltrate, or evapotranspirate stormwater and reduce flows to sewer systems.
green roofs
Green roofs, also called rooftop gardens, are a vegetative layer grown on a rooftop. Green roofs provide shade, remove heat from the air, and reduce temperatures on the roof surface and surrounding air; as such, they have been found to reduce the heat island effect and reduce building energy usage.
greenway
Greenways are open space corridors that can be managed for conservation, recreation, and alternative transportation. They usually follow natural or existing land or water features. They serve to connect people and communities, provide recreational outdoor space, link cultural and historic sites, provide refuge for wildlife, and numerous other benefits.
health impacts of climate change
Climate change influences human health and disease in numerous ways, and will intensify some existing health threats while creating new ones. Emerging health threats include respiratory and cardiovascular disease, injuries, premature deaths related to extreme weather events, changes in the prevalence and distribution of food and water-borne illnesses, and threats to mental health.
high-performance buildings
A high-performance building considers public building design, construction, and renovation programs that achieve certification using the U.S. Green Building Council's Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) green building rating standard or the Green Building Initiative's 'Green Gloes' building standard, or meets the requirements of VEES.
industrial waste
Industrial waste is an all-encompassing term used to describe material considered to be no longer of use after a manufacturing process has been completed. It can be hazardous or non-hazardous, although both can harm the environment if not properly managed. It can also include solid waste, toxic waste, chemical waste, and secondary waste (e.g., scraps, construction materials).
municipal energy management plan
Municipal energy management plans aim to reduce their city's energy usage through a strategic plan for local government operations. The typical goal of these plans is to reduce energy consumption by practicing energy efficiency and environmental stewardship across city operations. Most of these plans work within a SMART framework.
neighborhood amenities
Neighborhood amenities contribute to community life and enjoyment, and can include schools, stores, parks, and restaurants, for example. Families that live in neighborhoods with more of these community amenities tend to report more trust, sociability, and neighborliness and less loneliness and other maladies.
net-zero energy
Net zero energy is a concept defined by the use of energy conservation, energy efficiency, and on-site renewable generation to account for 100% of a targeted building’s or community’s energy usage.
organic waste
Organic waste is any material that is biodegradable and comes from either a plant or animal.
Portfolio Manager
Portfolio Manager is a tool created by the EPA to measure and track energy and water consumption and greenhouse gas emissions. It can be used to benchmark the performance of one building or a whole portfolio of buildings.
regeneration of ecosystems
Ecosystem regeneration seeks to restore the vital ecosystem services that play an important role in human society, such as providing food, drinking water, materials, and fuel, as well as broader climate regulation. Urban sustainable regeneration focuses on the complex interactions between urban environments and ecosystems and attempts to implement planning processes that consider both.
resilient infrastructure
Climate-resilient infrastructure is planned, designed, built, and operated in a way that anticipates, prepares for, and adapts to changing climate conditions. It can withstand disruptions caused by these climate conditions. It can include retrofits to existing infrastructure, new infrastructure, and new additional infrastructure such as sea walls.
retro-commissioning
Retrocommissioning is the first step in the building upgrade process. Commissioning outlines the interactions across all the energy flows in a building and produces a systematic method for planning upgrades that increase energy savings. It ensures that all systems are designed, installed, functionally tested, and capable of being operated and maintained according to the owner's needs, and retrocommissioning simply applies this process to existing buildings that have never been previously commissioned.
RVAH20
The RVA Clean Water Plan seeks to provide better administrative oversight over wastewater, stormwater, and drinking water utilities and services in the City of Richmond. Goals range from improving water quality and quantity, protecting and restoring aquatic and terrestrial habitats, and engaging the public to share responsibility for achieving a healthy watershed.
smart cities infrastructure
Smart cities are a framework, mostly comprising communication and information infrastructures and technologies, to develop, deploy, and promote sustainable development practices to address urbanization challenges. It facilitates a more interconnected city that can improve energy distribution, streamline trash collection, decrease traffic congestion, and improve air quality, for example.
transportation accessibility
Transportation accessibility measures how much you can get to in a given amount of time. It works jointly with transportation multimobility to determine the overall accessibility of a transportation system.
transportation demand management
Transportation Demand Management (TDM) focuses on understanding how people make their transportation decisions and helping people use the infrastructure in place for transit, ridesharing, walking, biking, and telework. It seeks to ensure that the design of transportation and physical infrastructure naturally encourages alternatives to driving.
transportation multimobility
Multimobility means combining a variety of transportation methods to move around.
upstream emissions
Upstream emissions are emissions that are generated from production and processing operations, rather than the direct burning of fossil fuels. These often rise the total energy expenditures of production processes, such as the extra upstream emissions required to dilute or heat bitumen in oil sands deposits.
Virginia Energy Conservation & Environmental Standards (VEES)
VEES are a series of conservation and environmental standards in place to guide construction and new development in Virginia.
vulnerability to climate change
Vulnerability to climate change encompasses physical, ecological, and social aspects that stem from increased extreme weather events, rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, sea level rise, and other aspects of climate on which the environment and human systems depend.